Create an environment
free from bullying
and
harassment



In today’s business landscape, the significance of respect within the workplace has never been more prominent. Australia’s Respect at Work Legislation provides comprehensive guidelines to cultivate respect and prevent harassment and discrimination at work.
Adhering to Respect at Work laws demonstrates a company’s commitment to a healthy, respectful workplace, which boosts employee satisfaction and strengthens a positive work culture.

Brief Overview
A critical aspect of the Respect at Work Act is that it requires businesses to actively prevent harassment and discrimination, thereby promoting a better work-life balance and safer work environments.



With the act already in effect, compliance isn’t a matter of choice but an absolute necessity.
The Australian Human Rights Commission (AHRC) offers a streamlined approach with specific principles and standards designed to enhance workplace cultures and improve employee engagement. Four guiding principles and seven essential standards support this approach: leadership, culture, knowledge, risk management, support, reporting and response, and transparency in monitoring and evaluation.
From 12 December 2023, the Commission will actively enforce and monitor these standards, aiming to increase productivity and reduce stress in workplaces across Australia.
The AHRC will use these guidelines as the benchmark for assessing compliance. You can access the detailed AHRC guidelines here.
The Historical Context & Recent Developments
Progress towards gender equality in Australia has been substantial. Yet, a concerning trend lingers: sexual harassment and gender inequality in the workplace.
A 2022 survey by the Australian Human Rights Commission found that one in three employees had experienced sexual harassment at work in the past five years, highlighting the urgent need to improve workplace communication and respect.
These alarming statistics led to the creation of the Anti-Discrimination and Human Rights Legislation (Respect at Work) Bill in November 2022, emphasising the need for businesses to actively foster a supportive work culture and manage employee turnover.

Understanding the Respect at Work Legislation

The Respect at Work Legislation establishes the legal framework for maintaining a respectful and positive working environment in Australia.
This legislation arose from the necessity to address overall workplace respect and sets out the legal boundaries within which companies must operate. The legislation’s objectives go beyond merely stopping harassment and eliminating sex discrimination; it aims to establish a culture where all team members feel respected from the outset.
The Respect at Work Legislation aims to prevent harassment and discrimination, promote fairness and equity, and protect the dignity of every employee, regardless of background or status. The laws also empower employees to stand against harassment and pursue justice without fear of retaliation, promoting a culture of safety and respect.
These laws guide employers on acceptable behaviour, demand cross-training and information, and outline how to handle complaints. On the other hand, these laws also encourage employees to oppose harassment and seek justice fearlessly, fostering a culture where people comfortably stand up against harassment and seek redress for grievances without fear of retaliation.
Understanding the Respect at Work Legislation
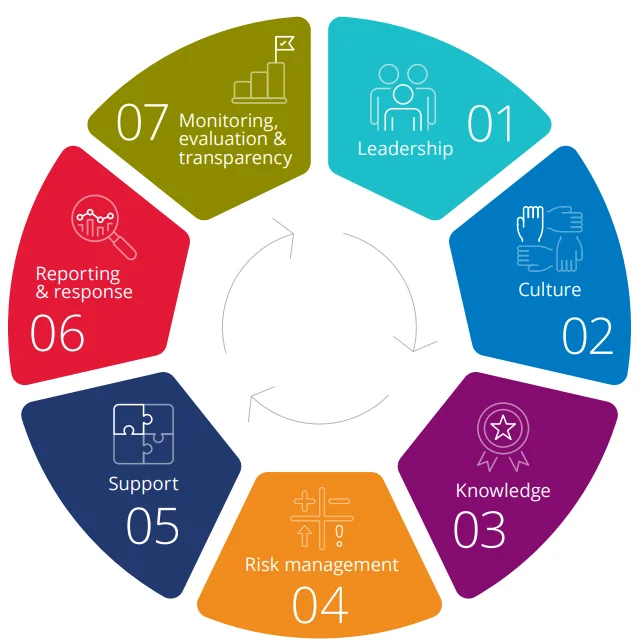
The table below sets out the seven Standards. The Commission explicitly states the responsibilities organisations have under the Sex Discrimination Act to foster better employee engagement.
The legislation includes practical examples that businesses can adopt to meet these standards and encourages involvement and idea-sharing among team members.
Rights And Responsibilities Under Respect At Work Laws
The Respect at Work Law outlines specific rights and responsibilities for both employees and employers.
✓ Employee Rights to a Respectful Workplace: The law ensures every individual receives treatment with dignity and respect. This includes protection against sexual, racial, or any other form of harassment in Australian workplaces.
✓ Employer Obligations in Preventing Workplace Harassment and Discrimination: Employers must take proactive measures to prevent inappropriate behaviours and provide clear reporting channels.
✓ Prohibited Behaviours and Actions Outlined in Respect at Work Legislation: The legislation clearly outlines behaviours that are considered harassing or discriminatory and provides guidelines on how to conduct oneself respectfully in the workplace.
✓ Legal Consequences for Non-Compliance with Respect at Work Laws: Ignoring these laws can result in fines, penalties, or other legal consequences for businesses.
Types Of Workplace Harassment And Discrimination
Understanding the various types of workplace harassment and discrimination is essential for both employers and employees.
✓ Overview of Different Forms of Harassment: This includes sexual harassment, racial discrimination, bullying, and more. Each form carries unique challenges and requires specific strategies to address.
✓ Examples of Discriminatory Practices in the Workplace: Discriminatory practices may include unfair promotions, biased hiring, unequal pay, and other overt or subtle actions.
✓ Recognising Subtle and Overt Acts of Harassment and Discrimination: Recognising both overt and subtle forms of harassment is essential for maintaining a positive and stress-free work environment.
✓ Psychological and Emotional Impact on Victims of Workplace Disrespect: Disrespect in the workplace can lead to serious mental health issues such as stress, anxiety, and depression, highlighting the need for a focus on employee well-being.
Preventing And Addressing Workplace Disrespect

Prevention is key to maintaining a respectful workplace, and it requires the collective efforts of the organisation.
✓ Establishing Comprehensive Anti-Harassment and Anti-Discrimination Policies: Businesses must develop detailed anti-harassment and anti-discrimination policies that are tailored to their specific workplace needs in compliance with the respect@work report.
✓ Promoting a Culture of Respect and Inclusion within the Organisation: Encouraging respectful communication and interaction is vital in cultivating a positive environment.
✓ Effective Training and Education Programs for Employees and Management: Education empowers employees to recognise and confront inappropriate conduct.
✓ Implementing Reporting Mechanisms and Whistleblower (Upstander) Protection: These must be established to encourage reporting and open communication, protect those who come forward from retaliation, and safeguard other team members as well.
Navigating Complaint Procedures And Investigations
Employers must handle allegations of disrespect with utmost care.
✓ Step-by-Step Guide for Reporting Workplace Disrespect or Harassment: Educate employees on how to report incidents and ensure they feel supported throughout the process.
✓ How Employers Should Handle and Investigate Complaints: Employers must take all complaints seriously and conduct investigations impartially.
✓ Legal Rights and Protections for Whistleblowers (Upstanders): Whistleblowers/Upstanders have legal protections, ensuring they can speak up without fear of revenge, leading to an opportunity for employees to contribute to a safer workplace. The law protects whistleblowers (Upstanders), and it prohibits any form of retaliation against them.
✓ Ensuring Fairness and Impartiality throughout the Investigation Process: The investigation process must be conducted transparently and fairly, adhering to established workplace legislation.
Consequences For Violating Respect At Work Laws

The consequences of violating Respect at Work Legislation are serious and complex.
✓ Potential Penalties and Fines for Non-Compliance: These may include monetary fines, mandatory training, and other punitive measures.
✓ Civil and Criminal Consequences for Severe Cases of Workplace Disrespect: Severe cases of workplace disrespect might lead to civil lawsuits or criminal charges against the perpetrators.
✓ Reputational Damage to Organisations Found in Violation: Companies found in violation of these laws face significant reputational damage, which can have long-lasting and widespread effects.
✓ The Role of Courts and Administrative Bodies in Enforcing Respect at Work Legislation: Courts and administrative bodies are essential in enforcing the Respect at Work Legislation and ensuring organisational compliance.
Promoting A Culture Of Respect And Inclusion

A culture of respect and inclusion transcends mere compliance with laws.
✓ Strategies for Fostering Respectful Interactions and Communication: Encourage empathy, active listening, and open dialogue.
✓ Empowering Bystanders to Address and Prevent Workplace Disrespect: Empower all team members to take a stand against inappropriate behaviour.
✓ Celebrating Diversity and Embracing Differences in the Workplace: Recognise and honour the unique perspectives and contributions of all staff.
✓ Long-term Benefits of Prioritising Respect and Inclusion: Focusing on respect and inclusion not only complies with the law but also enhances employee morale, productivity, and the overall success of a business.
The Role Of Leadership

Leaders within organisations hold the mantle of responsibility in championing this change. Leaders who fully commit to and implement these principles can transform their organisations into models of respect and inclusivity.
A Call To Action For Businesses
Understanding these guidelines is crucial, but implementing them is even more so. Recognising this, we at www.bullyology.com offer bespoke training tailored to your business’s unique requirements. This involves understanding the laws, taking action for compliance, and developing necessary policies.
Contact us if you need help ensuring that your business meets these standards and is a leader in workplace respect!
In Conclusion
The Respect at Work Legislation guides Australian businesses in creating respectful workplaces and maintaining inclusivity. Understanding these laws and recognising harassment helps businesses build respectful workplaces. By actively working to prevent and address workplace disrespect, organisations can build a thriving, respectful workplace.
Every individual, be they employer, manager, or employee, plays a crucial role in creating an inclusive work environment. It goes beyond mere legal compliance to foster a culture that values dignity, diversity, and collaboration. Building a workplace free from disrespect and discrimination is a journey we all share; driven by a collective commitment to empathy, understanding, and RESPECT!
The President of the Australian Human Rights Commission aptly summarises the vision for Australian workplaces – “An environment safe, inclusive, gender-equal, free from harassment, where all Australians, irrespective of their gender, race, orientation, disability, or age, can truly flourish.”
FAQ

Workplace disrespect can include a range of behaviours such as harassment, bullying, discrimination, unequal treatment, offensive language, or any other actions that create a hostile work environment. Respect at Work Legislation outlines specifically prohibited behaviours and provides guidance for acceptable conduct.
Employees can utilise internal reporting mechanisms, including anonymous reporting channels if available, provided by their employer. Respect at Work Legislation also offers legal protections for whistleblowers (Upstanders), ensuring they can report issues without fear of retaliation.
Yes, many jurisdictions under Respect at Work Legislation require employers to provide training and education to employees and management on the laws, rights, and responsibilities related to maintaining a respectful workplace.
Yes, Respect at Work legislation applies to businesses of all sizes, including small businesses. Compliance is required regardless of the size or industry of the organisation.
An employee can escalate the issue to higher management, seek assistance from their union if applicable, or report the matter to the relevant government agency responsible for enforcing Respect at Work Laws.
Yes, anonymous complaints should be taken seriously and investigated in accordance with the policies and Respect at Work Legislation. The anonymity of the complainant is respected, but the process should be transparent and thorough.
Yes, many cases of workplace disrespect can be resolved through alternative dispute resolution methods like mediation or arbitration. These methods often provide a more private and potentially quicker resolution.
Workplace respect fosters a positive environment, enhancing collaboration, trust, and satisfaction among employees. This leads to increased morale, engagement, and productivity, ultimately contributing to the overall success of the organization.
Employers can access information from government websites, legal firms specialising in employment law, human resource professionals, and various online platforms offering guidance and training related to Respect at Work Legislation.
Yes, depending on the severity and circumstances of the disrespect, an individual may have the legal right to file a civil lawsuit against their employer. This step should be considered carefully and usually with the guidance of a legal professional.
Keep Up To Date
SIGN UP NOW TO RECEIVE THE RESOURCES, INSPIRATION AND TOOLS TO HELP YOU STOP BULLYING AND HARASSMENT—WHETHER IN SCHOOLS, WORKPLACES OR ONLINE.


